7,162 rTSA-patient study demonstrates Equinoxe has the lowest aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening rate for any large-scale published rTSA outcome study1,2
Not All Reverses Are Created Equal
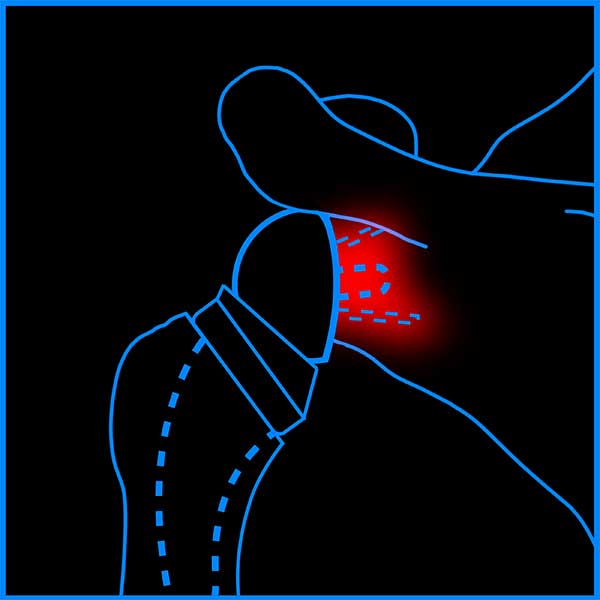
1.15%
Average Glenoid Loosening Rate of Medialized CoR rTSA2
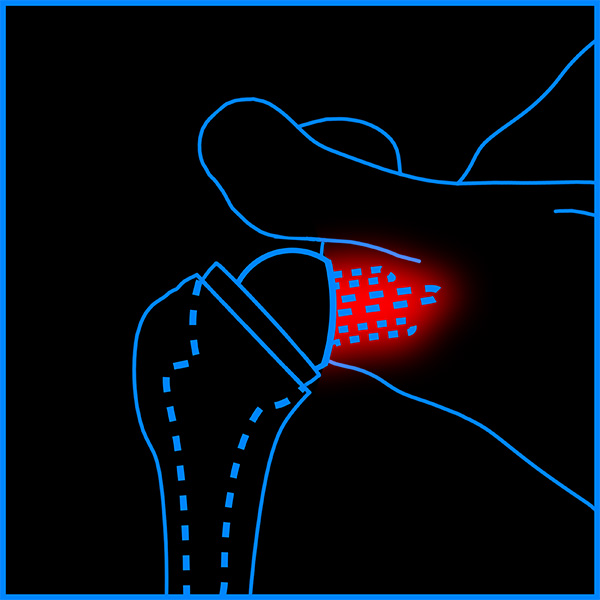
1.84%
Average Glenoid Loosening Rate of Lateralized CoR rTSA2
Patient rTSA Study
7,162 rTSA-patient study demonstrates Equinoxe has the lowest aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening rate for any large-scale published rTSA outcome study1,2

1.15%
Average Glenoid Loosening Rate of Medialized CoR rTSA2

1.84%
Average Glenoid Loosening Rate of Lateralized CoR rTSA2
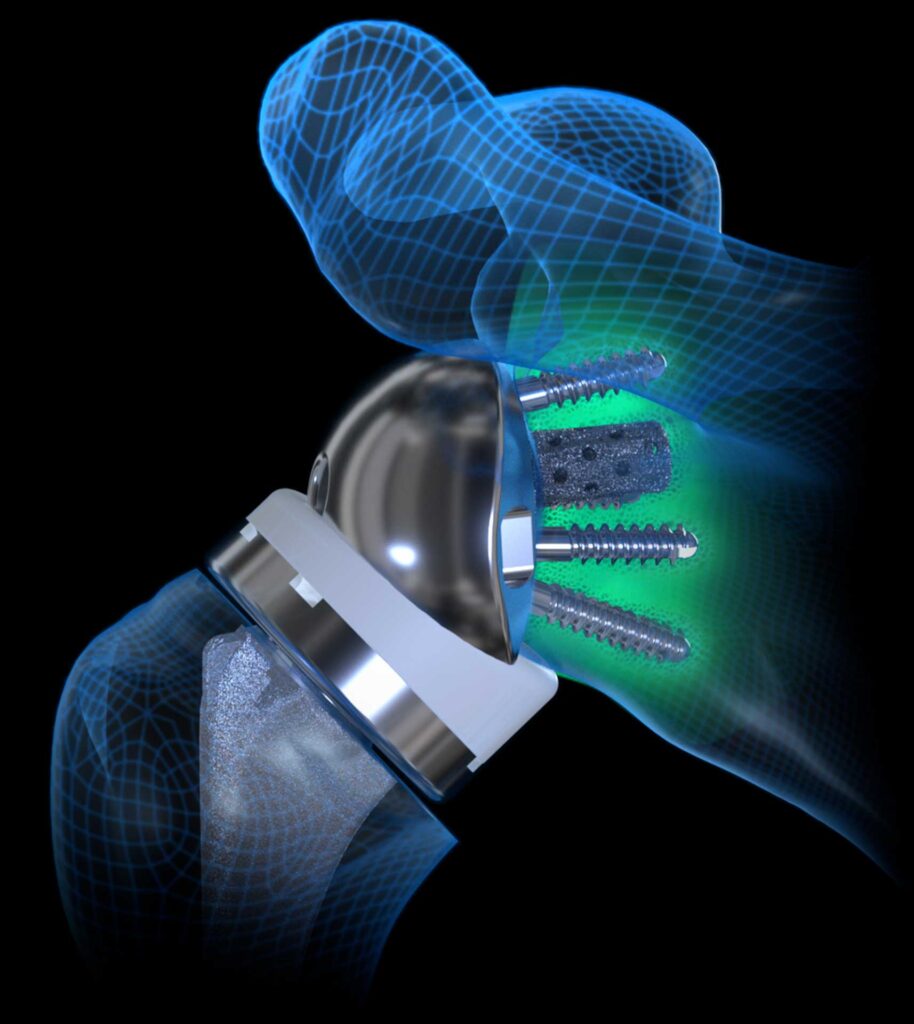
Aseptic Glenoid Baseplate Loosening after Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty with a Single Prosthesis
Early reverse total shoulder arthroplasty (rTSA) designs had high failure rates, mainly from loosening of the glenoid baseplate. The purpose of this study is to determine the incidence of aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening after primary rTSA using a contemporary medialized glenoid/lateralized humeral system and identify significant risk factors associated with loosening.
7,162 primary rTSA were treated with a single platform rTSA system between April 2007 and August 2021, from which 3,127 primary rTSA patients with a minimum 2-year follow-up were identified. Patients with aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening were compared to all other primary rTSA without loosening. Univariate and multivariate analyses were performed to compare these cohorts and identify the demographic, comorbidities, operative, and implants associated aseptic glenoid loosening after rTSA. Odds ratios were calculated for each significant risk factor and for multiple combinations of risk factors.
Irrespective of minimum follow-up, fifty-three (31F/22M) of 7,162 primary rTSA shoulders experienced aseptic glenoid loosening, for an overall rate of 0.74%. At latest 2-year minimum follow-up, thirty of 3,127 patients experienced aseptic glenoid loosening and had significantly lower clinical scores, function, active ROM, and higher pain scores as compared to patients without loosening. Univariate analysis identified that patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA, p=0.029, OR = 2.74) and diabetes (p=0.028, OR=1.84) and multivariate analysis identified Walch glenoid types B2 (p=0.002, OR= 4.513) and B3 (p=0.002, OR=14.804), use of expanded lateralized glenospheres (p=0.025, OR=2.57) and use of augmented baseplates (p=0.001, OR=2.50) as significant risk factors for aseptic glenoid loosening after rTSA.
The incidence of aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening was 0.74% for this medialized glenoid/lateralized humeral rTSA system. Numerous risk factors for aseptic loosening were identified, including: RA, diabetes, Walch B2 and B3 glenoids, posterior/superior augmented baseplates, and expanded lateralized glenospheres. Finally, analysis of multiple combinations of risk factors identified patients and implant configurations with the greatest risk of aseptic glenoid loosening.
- Schell LE, Roche CP, Eichinger JK, Flurin PH, Wright TW, Zuckerman JD, Friedman RJ. Aseptic glenoid baseplate loosening after reverse total shoulder arthroplasty with a single prosthesis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2023 Feb 2:S1058-2746(23)00065-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2023.01.010.
- Jorge Rojas, MD; Kyubo Choi, MD; Jacob Joseph, BA; Uma Srikumaran, MD; Edward G. McFarland, MD. Aseptic Glenoid Baseplate Loosening After Reverse Total Shoulder Arthroplasty: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Bone Joint Surg. 2019 May;7(5):e7. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.RVW.18.00132.